Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) with exceptionally high purity (>99.9%) are synthesized using the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method. A subsequent annealing process at approximately 3000 °C for around 24 hours (graphitization) enhances their purity and significantly improves their electrical and thermal conductivity.
Due to their excellent conductive and mechanical properties, carbon nanofibers are considered a highly promising material, comparable to carbon nanotubes. They are widely studied and utilized in various applications, including chemical catalysis, energy conversion, hydrogen storage, rechargeable batteries, electrodes, lithography, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, supercapacitors, sensors, displays, biomedical research, and polymer/composite reinforcement.
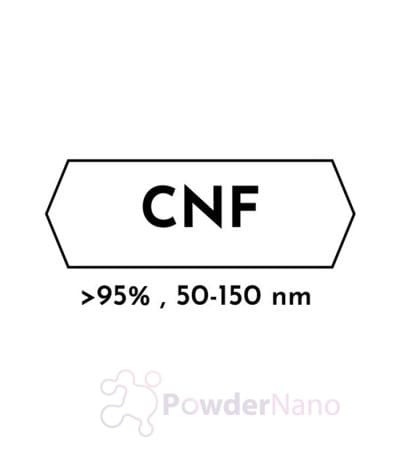
Technical Properties of Carbon Nanofibers (CNFs)
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance (Color) | Black |
| pH Range | 5.5 – 8.5 |
| Ash Content | Less than 0.1% |
| Bulk Density | 0.039 g/cm³ |
| True Density | 2.1 g/cm³ |
| CNF Dimensions | Outer Diameter: 200–600 nm Length: 10–50 µm |
| Specific Surface Area | 20 m²/g |
| Electrical Conductivity | 110 S/cm |